
In the world of health and fitness, the term macros is often mentioned, but what exactly does it mean? In simple terms, macros refer to macronutrients, the three main components of our diet that provide the energy and nutrients needed for various bodily functions. These include proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Understanding how to balance and optimize these macronutrients is crucial for anyone looking to improve their overall health, achieve fitness goals, or simply maintain a balanced diet. In this guide, we will explore each of these macronutrients in depth, how they impact our body, and how to incorporate them into a well-rounded, nutritious diet.
What Are Macros?
Macros, short for macronutrients, are essential nutrients that our bodies need in large amounts to function properly. They provide the energy necessary for everything from basic bodily functions to intense physical activities. Each type of macronutrient serves a unique role in maintaining health and fitness.
The three primary macronutrients are:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
Each of these macronutrients has its own specific function, and it’s important to understand their role in your overall nutrition to make informed decisions about your diet.
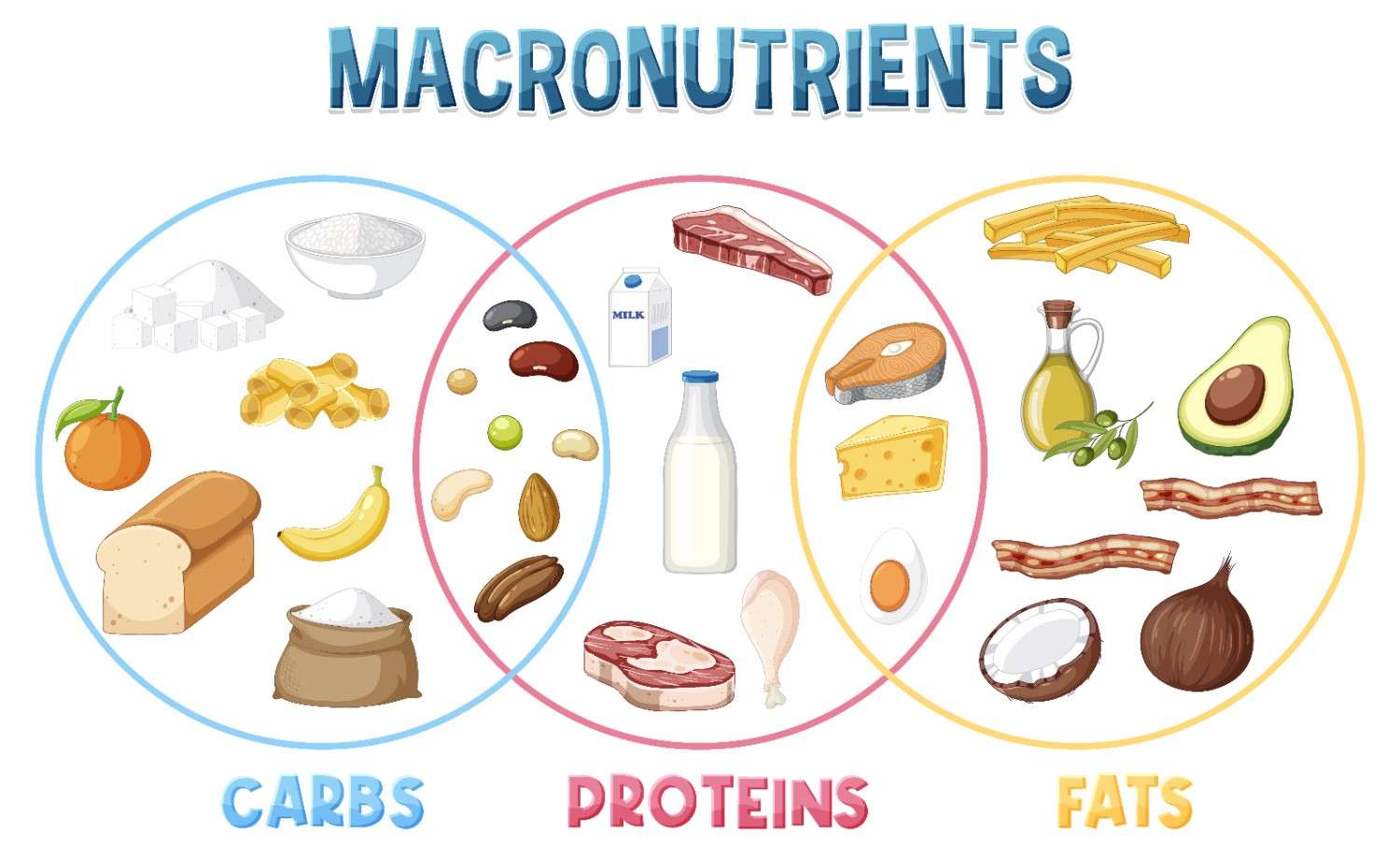
Carbohydrates: The Body’s Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the body’s main energy source. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose (sugar), which is then used by the body for energy. Carbohydrates are essential for high-intensity activities like running, weightlifting, or sprinting. There are two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex.
- Simple carbohydrates: Found in foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, these carbs are quickly absorbed by the body and provide fast energy. However, they can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Complex carbohydrates: Found in whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables, these take longer to break down, providing a steady source of energy over time. They also tend to be richer in fiber, which aids digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Proteins: The Building Blocks of the Body
Proteins are crucial for building, repairing, and maintaining tissues, muscles, and organs. Proteins are made up of amino acids, some of which are essential and must be obtained through food. Protein is important for muscle growth, immune function, and hormone production.
Some excellent sources of protein include:
- Animal-based proteins: Chicken, turkey, beef, fish, eggs, and dairy
- Plant-based proteins: Tofu, lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, and edamame
While animal proteins tend to be more complete, meaning they contain all the essential amino acids, plant-based proteins can also provide the necessary building blocks when combined properly.
Fats: The Essential Nutrient for Hormone Function
Fats have often been demonized in the past, but they are actually essential for good health. Fats provide long-lasting energy, support cellular function, and are necessary for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Fats also play a key role in hormone production and the regulation of body temperature.
There are three main types of fats:
- Unsaturated fats: These are considered the healthiest fats. They are found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Unsaturated fats can help lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Saturated fats: Found in animal products like butter, cheese, and fatty cuts of meat, as well as tropical oils like coconut oil and palm oil. While they are necessary in small amounts, excessive consumption of saturated fats can lead to heart disease.
- Trans fats: These are artificially created fats found in processed foods and should be avoided as they increase the risk of heart disease and other health problems.
How to Balance Your Macros
Balancing macros effectively depends on your personal health goals, activity level, and body type. A general rule of thumb for healthy individuals is:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of your total daily calories
- Proteins: 10-35% of your total daily calories
- Fats: 20-35% of your total daily calories
However, individuals with specific goals—such as building muscle, losing weight, or improving athletic performance—may need to adjust these ratios.
For example, someone looking to build muscle might increase protein intake, while someone focused on weight loss may opt for a higher fat and lower carbohydrate approach. A certified nutritionist or dietitian can help personalize these recommendations based on your unique needs.
Benefits of Tracking Macros
Tracking your macros can provide several benefits, especially for those looking to optimize their diet for specific goals. By being mindful of your macronutrient intake, you can:
- Improve body composition: Balancing your macronutrients helps you maintain a healthy weight, build lean muscle, and reduce body fat.
- Optimize energy levels: Properly balanced macros ensure your body has the energy it needs for physical activity and day-to-day functions.
- Prevent nutrient deficiencies: Tracking macros can help ensure you are consuming a well-rounded diet and getting all the necessary nutrients your body requires.
- Boost performance: For athletes, balancing macronutrients appropriately can enhance endurance, strength, and recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I calculate my macros?
To calculate your macros, start by determining your total daily calorie needs (based on factors such as age, gender, weight, height, and activity level). Once you know your calorie needs, you can apply the recommended percentage ranges for each macronutrient. For example, if your goal is to consume 2,000 calories per day and you want 50% of those calories to come from carbohydrates, you would consume 1,000 calories from carbs, which equals approximately 250 grams of carbohydrates.
2. Should I focus on macronutrients or micronutrients?
Both macronutrients (carbs, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) are essential for health. However, macronutrients provide the bulk of your energy needs. It is important to strike a balance by focusing on both macronutrient ratios for energy and micronutrient-rich foods to ensure overall health and well-being.
3. Can I eat carbs and still lose weight?
Yes, carbohydrates are not inherently fattening. It is important to focus on the quality of carbs you consume, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, rather than processed sugars and refined grains. Balancing your overall calorie intake and maintaining a healthy deficit is key to losing weight.
4. How do I adjust my macros for weight loss?
For weight loss, you may want to reduce carbohydrate intake slightly while maintaining an adequate protein intake to preserve muscle mass. Increasing fat intake can help keep you feeling full longer. Remember that the key to weight loss is creating a calorie deficit, so tracking your total calorie intake is just as important as managing your macros.
Macros in Different Diets
Different diets emphasize varying proportions of macronutrients. Here are a few examples:
- Keto diet: Focuses on high fats (70-80%), moderate protein (20-25%), and very low carbs (5-10%).
- Low-carb diet: Typically consists of around 30-40% carbs, with higher protein and fat intakes.
- Balanced diet: Follows the typical macro ratio of 45-65% carbs, 10-35% protein, and 20-35% fat.
The Key Takeaway
Understanding and properly balancing your macronutrients is essential for optimizing your diet and achieving your health and fitness goals. Whether you’re looking to lose weight, build muscle, or simply maintain a healthy lifestyle, tracking your macros can help you stay on track. By incorporating the right balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, you can enhance your performance, improve your body composition, and ensure long-term health.


